RAN is an essential component of mobile communication infrastructure. which is commonly known to the public as the base station when viewed from visible perspective. The "Open" refers to its open architecture. The Open RAN market is estimated to reach $3.18 billion in 2025, accounting for approximately 8% to 10% of the total RAN market revenue. It is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 32.11% to $38.71 billion by 2034 Note1.
Note1:Precedence Research; Telecomled
Delta’s Advanced Millimeter Wave Systems Business Division (AMSBD) was established in late 2018 and is dedicated to developing technologies and products for Radio Units (RU). The RU is a device in an Open RAN that transmits and receives wireless signals to communicate with mobile devices, playing a decisive role in wireless network coverage and performance. With the growth trend of the Open RAN market, it is expected that Delta will have another growth momentum in its telecom infrastructure-related business.
RAN is a crucial component of mobile communication infrastructure
In the growth trend of Open RANNote 2, governments, telecom operators, and industry alliances drive market development. Since the China-US trade war in 2018, many countries have begun supporting the open structure of Open RAN to avoid excessive dependence on single vendors, which could create national security vulnerabilities. Government departments are encouraging telecommunications operators and supply chains to accelerate the development of Open RAN networks in regional markets through subsidies and competitions.
Note2: O-RAN Alliance
The United States passed the USA Telecommunications Act back in 2020, and has been promoting the development of Open RAN since 2023 through a US$1.5 billion investment via the Public Wireless Supply Chain Innovation Fund, encouraging telecommunications operators to adopt Open RAN technology and providing financial subsidies for related technologies.
The Japanese government passed the Act on Promotion of Developing/Supplying and Introducing Systems Making Use of Specified Advanced Information Communication Technologies through the National Diet of Japan in 2022. This has encouraged companies to deploy equipment with internationally certified open architecture by providing tax rebates. Additionally, the government provides facilities for related companies to conduct research and testing. Japan has also developed the "Global Promotion Action Plan 2025," which declares their vision of using 5G O-RAN for global high-speed internet, allocating 20 billion yen to hire Japanese manufacturers to jointly develop high-quality O-RAN network technology.
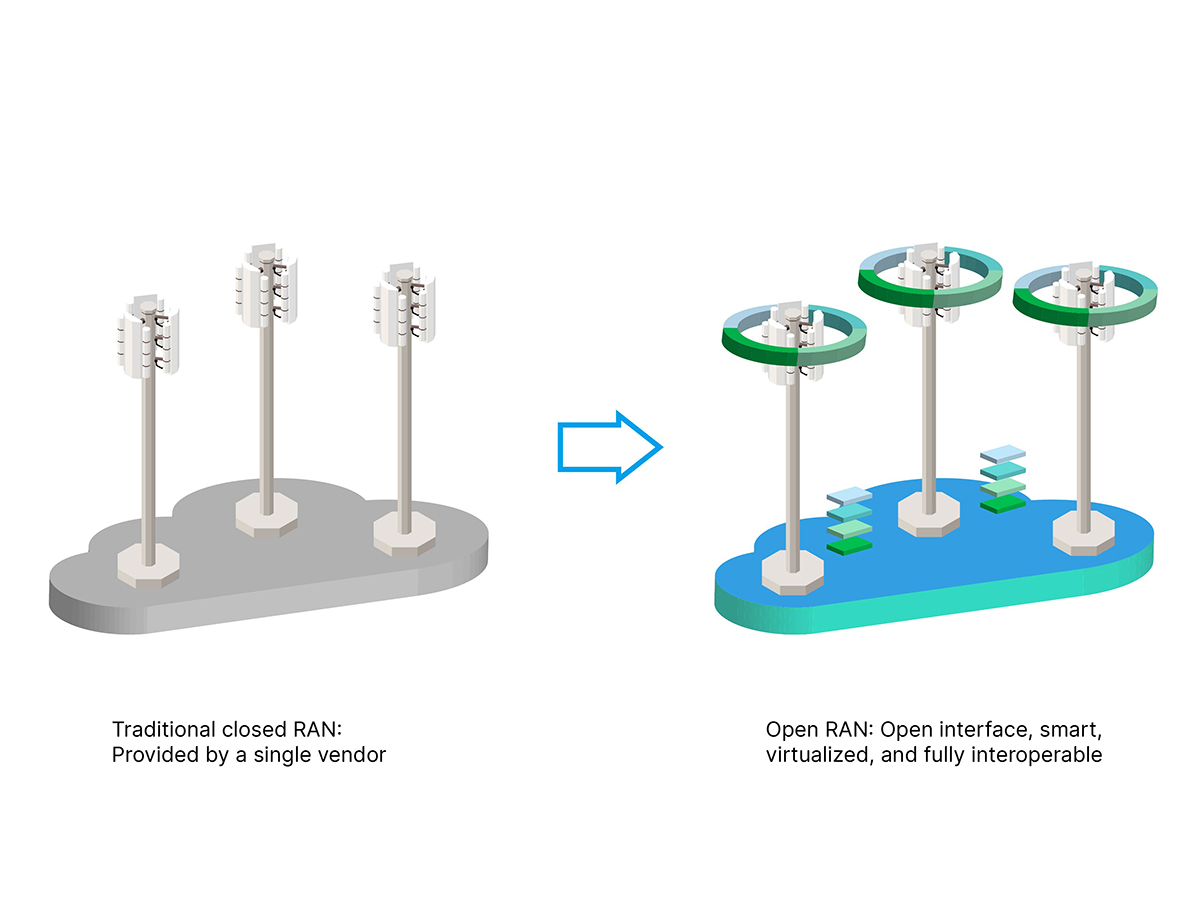 Breaking free from traditional equipment vendor control: telecom operators turning to Open RAN
Breaking free from traditional equipment vendor control: telecom operators turning to Open RAN
Traditional RAN equipment vendors such as Huawei, Ericsson, Nokia, and ZTE collectively account for approximately 85% of the RAN market share. Telecom operators, as the end customers of RAN, need to constantly upgrade and maintain network equipment to maintain stable connection quality, extensive network coverage, and efficient data transmission for their service networks to meet the growing demands of mobile data connectivity. However, with limited growth in consumer payments for telecommunications services, adopting Open RAN has become one of the important strategies for telecommunications operators to reduce operating costs.
Open RAN's core concept is to allow equipment from different vendors to interoperate through open and standardized interfaces, thereby breaking the monopoly of traditional proprietary equipment and promoting innovation and competition. This not only frees telecom operators from the control of traditional equipment vendors but also reduces their deployment and maintenance costs. Examples of telecom operators advancing Open RAN through actual investment cases in 2024 are as follows:
In early 2024, AT&T, one of the three major telecom operators in the United States, signed a five-year contract with Ericsson, investing $14 billion to begin transitioning AT&T's RAN toward an Open RAN network architecture starting in 2024.
In mid-2024, KDDI and SoftBank, Japan's second and third largest telecom operators, committed to jointly building a total of 100,000 5G base stations by fiscal year 2030 through their joint venture 5G JAPAN Corporation. Subsequently, KDDI selected Samsung's virtualized RAN solution to expand its Open RAN deployment starting from 2025Note3.
Note3: Samsun Newsroom
In late 2024, MasOrange, Spain's largest telecommunications operator, signed a 5G Open RAN agreement with Ericsson, planning to deploy Open RAN technology on approximately 10,000 base stations. Deutsche Telekom signed an Open RAN contract with Nokia, planning to deploy Open RAN technology on at least 3,000 base stations within Germany to replace equipment previously provided by Huawei.
Traditional equipment vendors join the Open RAN trend
Traditional equipment vendors' customers, leading global telecommunications operators, are requiring Ericsson and Nokia to invest resources through actual contracts to establish an Open RAN ecosystem, open interfaces, and provide diverse Open RU options, gradually converting RAN deployments to Open RAN year by year.
O-RAN Alliance promotes the development of the pen RAN industry
The O-RAN Alliance is an open international standards organization composed of telecommunications operators, vendors, and research and academic institutions with over 300 members. Since its establishment in 2018, it has been dedicated to promoting the standardization of Open RAN. The organization defines O-RAN specifications, standardized interface protocols, the O-RAN software community, and provides integration testing services and tools, enabling RAN equipment from different vendors to interoperate seamlessly. The O-RAN Alliance held the O-RAN ALLIANCE Summit at MWC in Barcelona in March 2025, which comprehensively introduced the current status of O-RAN, operational experiences, regional perspectives and important projects, as well as applications in vertical industries, and discussed how 3GPP and O-RAN architectures will evolve toward the future of 6G.
Government policies, technological innovation, partnerships, and standardization all support the continued growth of Open RAN, and this trend is expected to fundamentally change the landscape of the global telecom industry within the next five years.















