With the accelerated pace of global digital transformation, information security has become a critical factor in business development, and product information security is gaining increasing attention. The core of this issue is to ensure product security throughout the phases of design, manufacturing, operation, and maintenance, preventing risks such as malicious attacks, data theft, or system disruptions.
Scope of product information security
Product information security involves multi-layered protection that spans from hardware to software. At the hardware level, it includes anti-tampering design and securing the supply chain for devices; at the software level, it covers operating system security, application protection, and communication protocol encryption. The scope of information security is broad, necessitating close attention to compliance, supply chain security, software and hardware security, and network security throughout the entire product lifecycle.
In terms of compliance, companies must ensure that products adhere to relevant information security standards and regulations during design, development, and operational phases. Supply chain security focuses on ensuring that all suppliers comply with security standards, preventing attackers from exploiting vulnerabilities in the supply chain. Hardware security aims to prevent unauthorized tampering with physical components, including protection against reverse engineering and safeguarding chips and printed circuit boards. Software security is concerned with preventing malicious software, exploiting vulnerabilities, and unauthorized access; it ensures software integrity through encryption, secure updates, and prevention of backdoors. Since smart products rely on network connectivity for data transmission, network security safeguards the network connected to the product from becoming an entry point for attacks and prevents unauthorized devices from accessing the network.
 With the accelerated pace of global digital transformation, information security has become a critical factor in business development, and product information security is gaining increasing attention.
With the accelerated pace of global digital transformation, information security has become a critical factor in business development, and product information security is gaining increasing attention.
Regulatory and technological trends
Regulatory trends primarily focus on addressing rapidly evolving network threats and enhancing digital resilience. In recent years, government agencies have strengthened information security requirements for critical infrastructure and IoT devices, promoting zero-trust architectures. International standards like IEC 62443 have also become critical benchmarks for device suppliers seeking product certifications. Additionally, regulatory trends include heightened oversight of supply chain security, ensuring that all stages are equipped with the necessary information security protections. Countries have introduced stricter product information security standards, such as the U.S. NIST SP 800-53, the E.U.’s NIS 2.0 Directive, and SEMI E187 for semiconductor equipment security. These standards mandate companies to embed information security into the early stages of product development to ensure secure management across the entire product lifecycle. The IEC 62443 standard for industrial control systems has become a key compliance indicator in the industrial automation field. With increasing global reliance on IoT devices and smart manufacturing, future compliance requirements for information security are expected to become even more rigorous.
In terms of technological trends, information security technologies are advancing towards the integration of zero-trust architectures with artificial intelligence (AI). Zero-trust architecture has become essential for addressing modern information security threats, based on the principle of "trust no one or any device." Even within internal networks, all devices and users must undergo authentication and authorization. AI, in turn, leverages data analysis to quickly detect abnormal behavior and potential threats, providing automated threat mitigation capabilities that enhance information security defenses. Additionally, Application Whitelisting and Software Bill of Materials (BOM) are vital tools for ensuring product information security. Application Whitelisting prevents unauthorized applications from running by only allowing approved ones, which is especially effective in industrial control systems as it significantly reduces attack risks. As the importance of software supply chain security grows, Software BOM helps businesses trace software sources, enabling prompt identification and patching of potential information security vulnerabilities.
With the rapid growth in global demand for product information security, the Delta Research Center (DRC) is actively expanding its technical expertise and service offerings in this field. DRC has accumulated valuable experience in information security compliance services for standards such as SEMI E187, IEC 62443, and TW EV Cybersecurity. In early 2024, DRC completed the compliance process for UI FusionX, addressing the SEMI E187 requirements for Universal Instrument (UI) through gap analysis and vulnerability assessment. Currently, no single information security vendor in the market can provide such a comprehensive, one-stop SEMI E187 compliance service. Furthermore, the recent focus has been on the research, development, and application of product information security technology, actively driving the development of technical solutions such as endpoint security, application whitelisting, and software bill of materials (BOM). By combining its information security compliance services with product information security technologies, Delta has established a new business group dedicated to product information security, aiming to continue providing protective solutions for various business groups while also offering information security solutions externally, further expanding Delta’s footprint in the product information security sector.
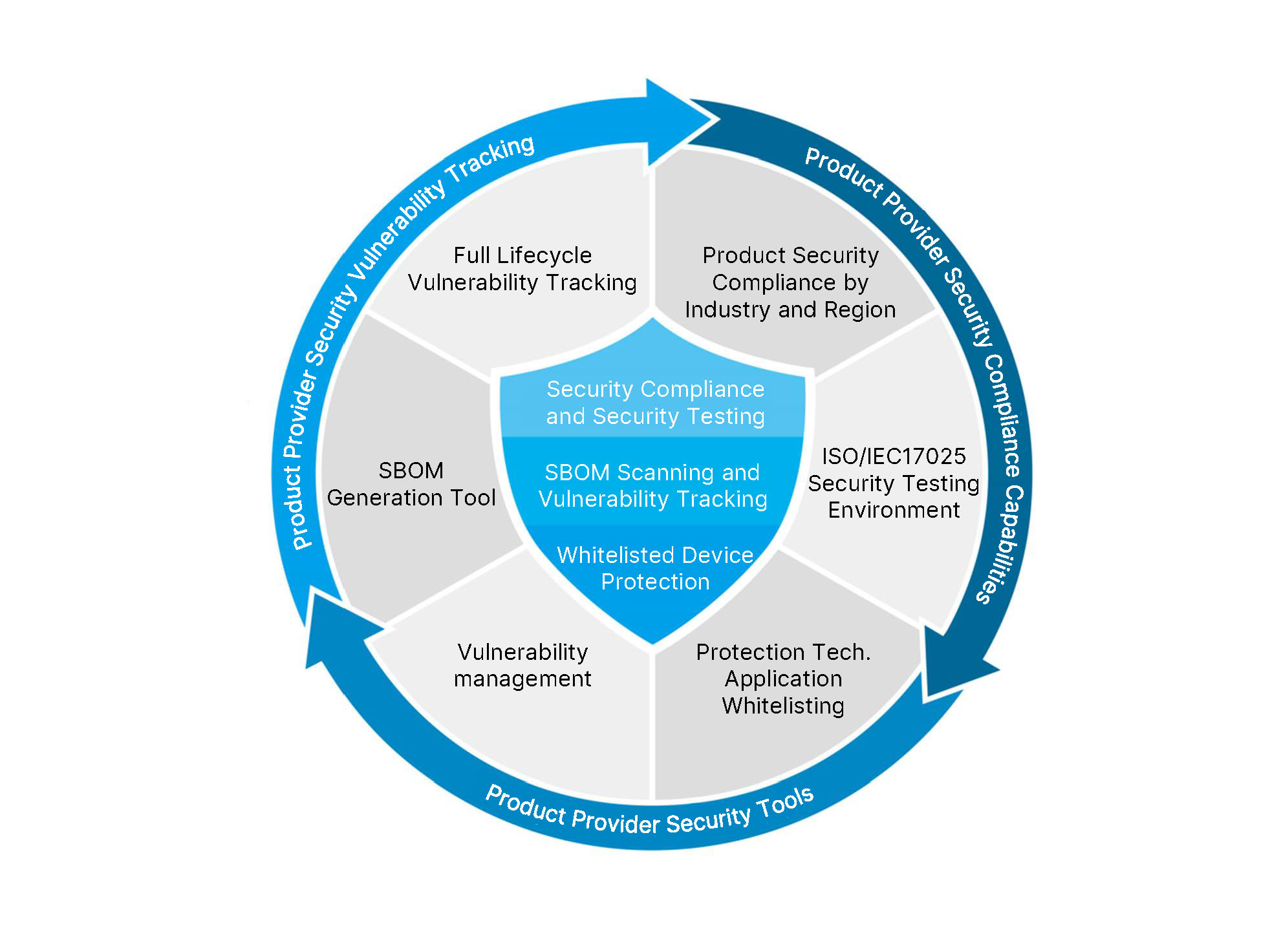 Delta has developed a comprehensive approach to product cybersecurity compliance through its one-stop compliance and assessment solutions.
Delta has developed a comprehensive approach to product cybersecurity compliance through its one-stop compliance and assessment solutions.















